Virtual high-resolution MRA from non-angiographic multi-contrast MRIs: synthetic vascular model populations for in-silico trials
Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) is a medical method that takes detailed pictures of blood vessels in the body. These pictures help doctors see how blood flows through arteries and veins.
However, MRA takes a longer time to do compared to some other tests like X-rays. So, even though it's good at showing blood vessels, doctors don't always use it as the first choice. They use it when they really need to see the blood vessels in detail, even if it means the test takes longer.
This research is about creating realistic, detailed images of blood vessels in the brain using a type of medical imaging called Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA). MRA images are essential for studying blood vessels in the brain, but they can be challenging to produce. This study introduces a new computer system that can make these MRA images from more common types of brain scans, like T1, T2, and PD-weighted MR images.
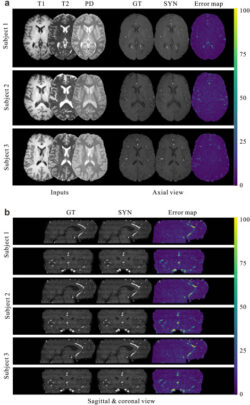
Fig. 3. Qualitative evaluation of the proposed method. (a) Visual comparison of the generated 2D MRA axial slices to the ground-truth MRA slices from three representative subjects. (b) Results of the same subjects in the sagittal and coronal views. The comparison is also augmented by the error maps shown in the rightmost column.
Fig. 3. Qualitative evaluation of the proposed method. (a) Visual comparison of the generated 2D MRA axial slices to the ground-truth MRA slices from three representative subjects. (b) Results of the same subjects in the sagittal and coronal views. The comparison is also augmented by the error maps shown in the rightmost column.
This makes it easier for researchers to create digital models of the blood vessels in the brain for scientific studies. This can be helpful for simulating medical scenarios or experiments without involving real patients.
We built a computer programme that can learn from different types of brain images and then generate realistic digital twins. We also used a mathematical method to make sure the new images match the important features of blood vessels.
The results of the experiments show that their system can create high-quality MRA images and perform better than other methods. We found that some types of brain images, like T2 and PD-weighted images, are better for making MRA images than T1 images. The system can also work with data from different medical centers and scanners, and it can maintain the continuity of blood vessels in the images.
In summary, this research offers a new way to make detailed pictures of blood vessels in the brain, which can be valuable for scientific studies and medical research on a large scale.
Authors - Yan Xia, Nishant Ravikumar, Toni Lassila, Alejandro F. Frangi
